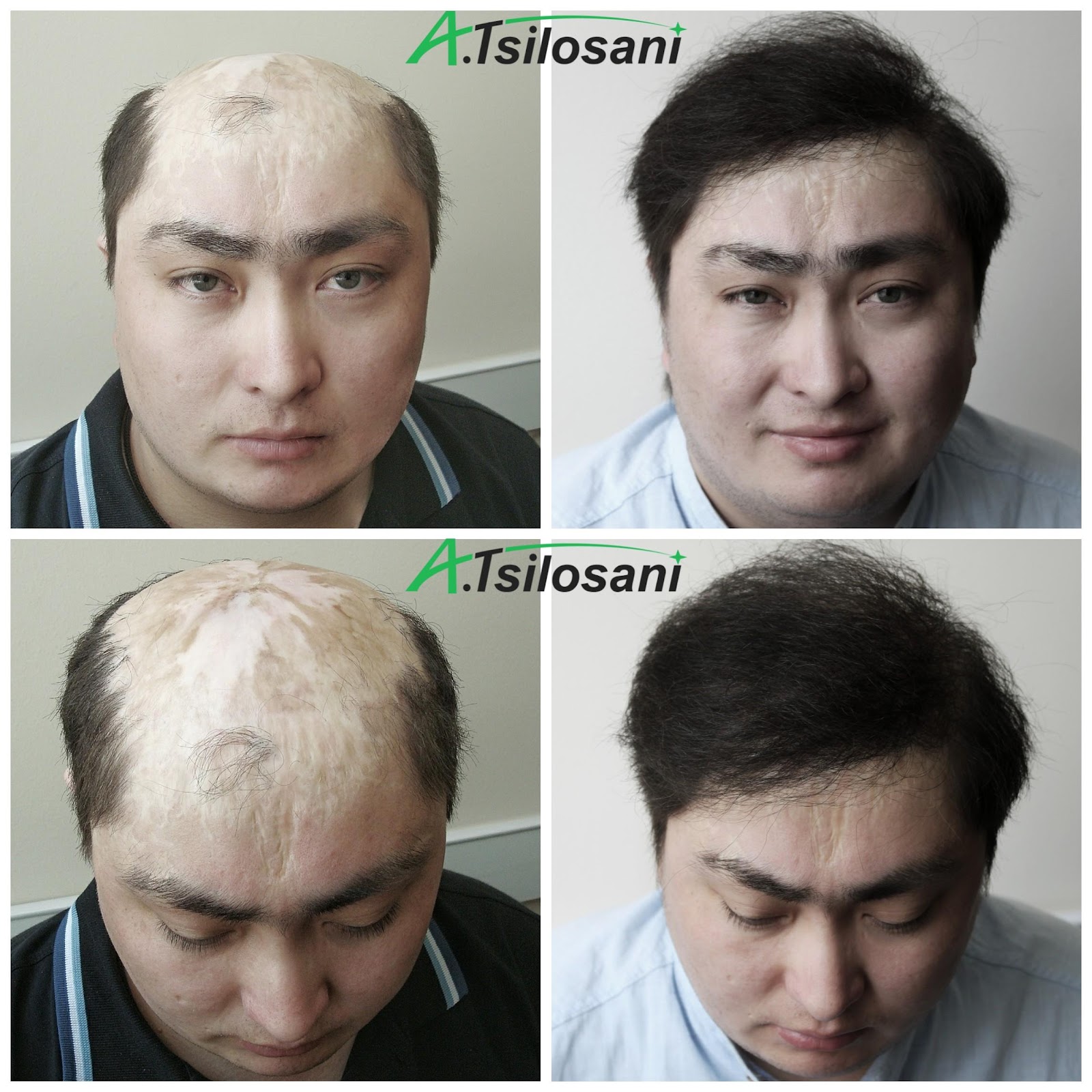
FUE transplantation (Follicle Unit Excision)
FUE transplant is a minimally invasive method of hair transplantation. The donor material is taken from the back of the head or other parts of the body (beard, chest, groin, legs, etc.) in the form of individual follicular units (grafts) using small (up to 1 mm in diameter) twisting punches.
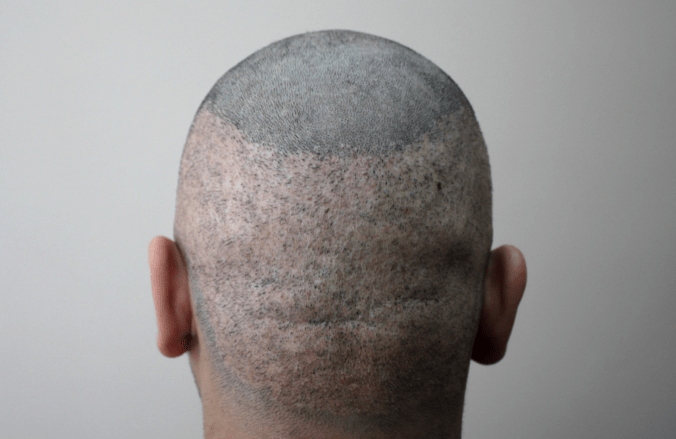
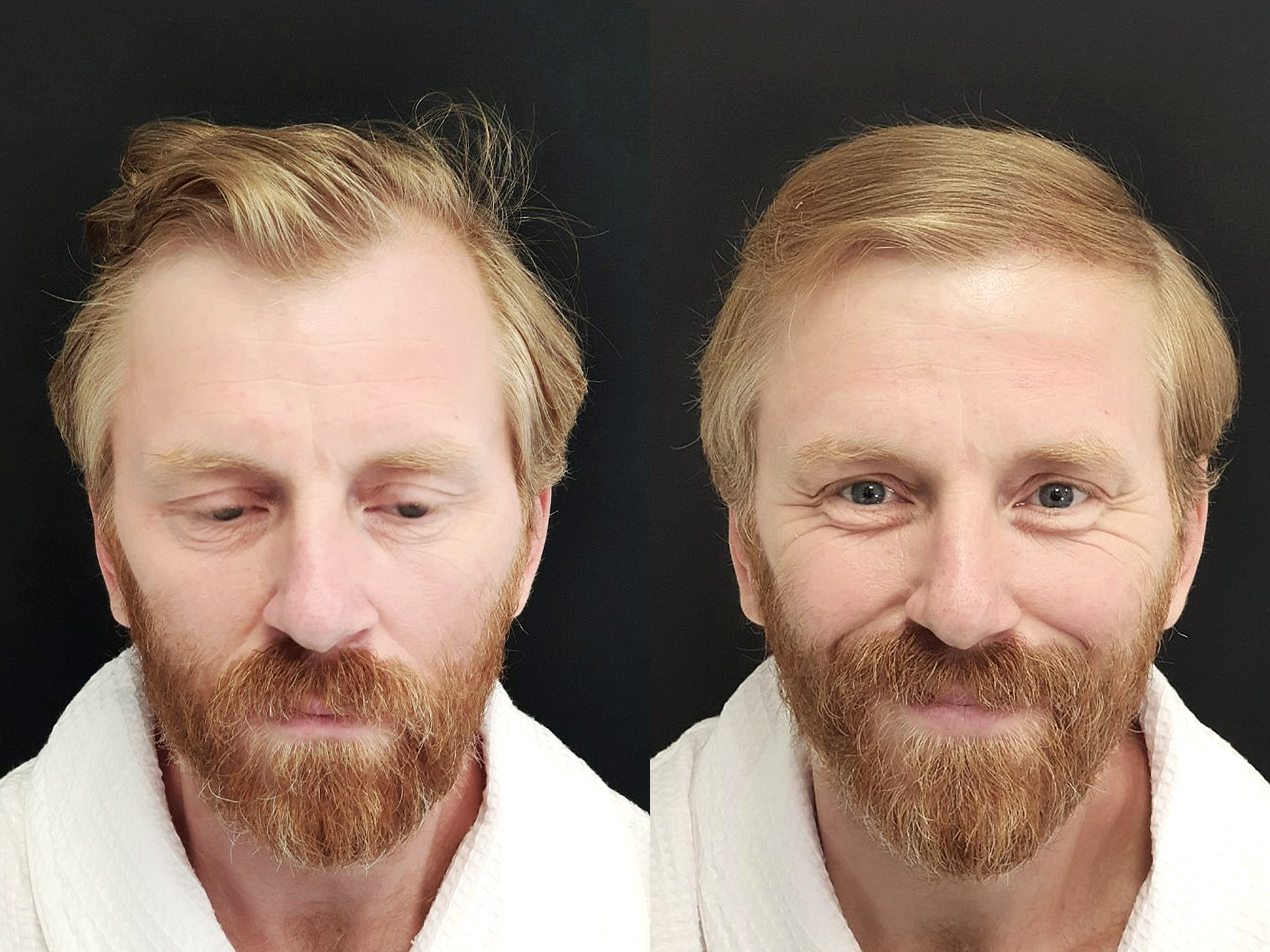
During FUE transplant technique, the surgeon makes circular, superficial (2-4 mm deep) incisions with the punch around each follicular unit after which the surgeon's assistant extracts them one by one using special forceps. Small wounds (up to 1 mm in diameter) left after the excision of follicular units are quickly healed leaving dot-like micro scars (see photos 1, 2, and 3). That’s why hair transplant recovery timeline after FUE transplant is shorter than after FUT technique. The main advantage of FUE transplant is that, unlike the FUT method, FUE leaves no linear scar on the back of the head and as already mentioned has shorter hair transplant recovery timeline. Otherwise FUE hair transplant side effects are the same as after FUT hair transplant method: numbness in donor area (till two months), shock loss (increasing of the persisting hair loss during the first month after the procedure) and folliculitis which rarely appears in the recipient area (one month after FUT or FUE hair transplant procedure). You can see FUE transplant before and after photos in our photo gallery. Approximately half of these photos belong to the patients who underwent FUT transplantation and half of those with FUE transplant. We assure you that you will not be able to distinguish which of those techniques have been performed on them.
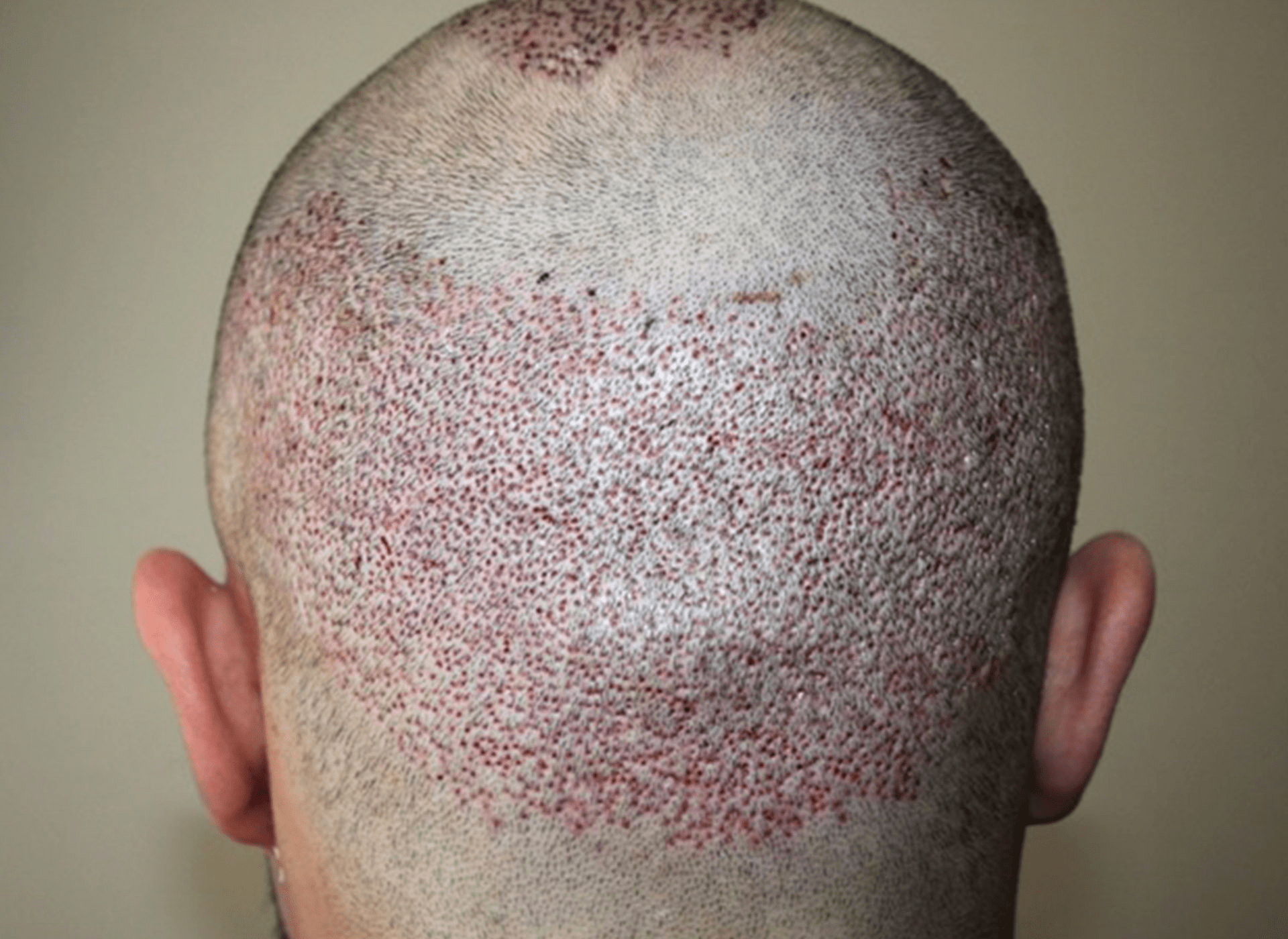
Photo 1. The donor area immediately after harvesting 3,000 grafts with the FUE transplant method
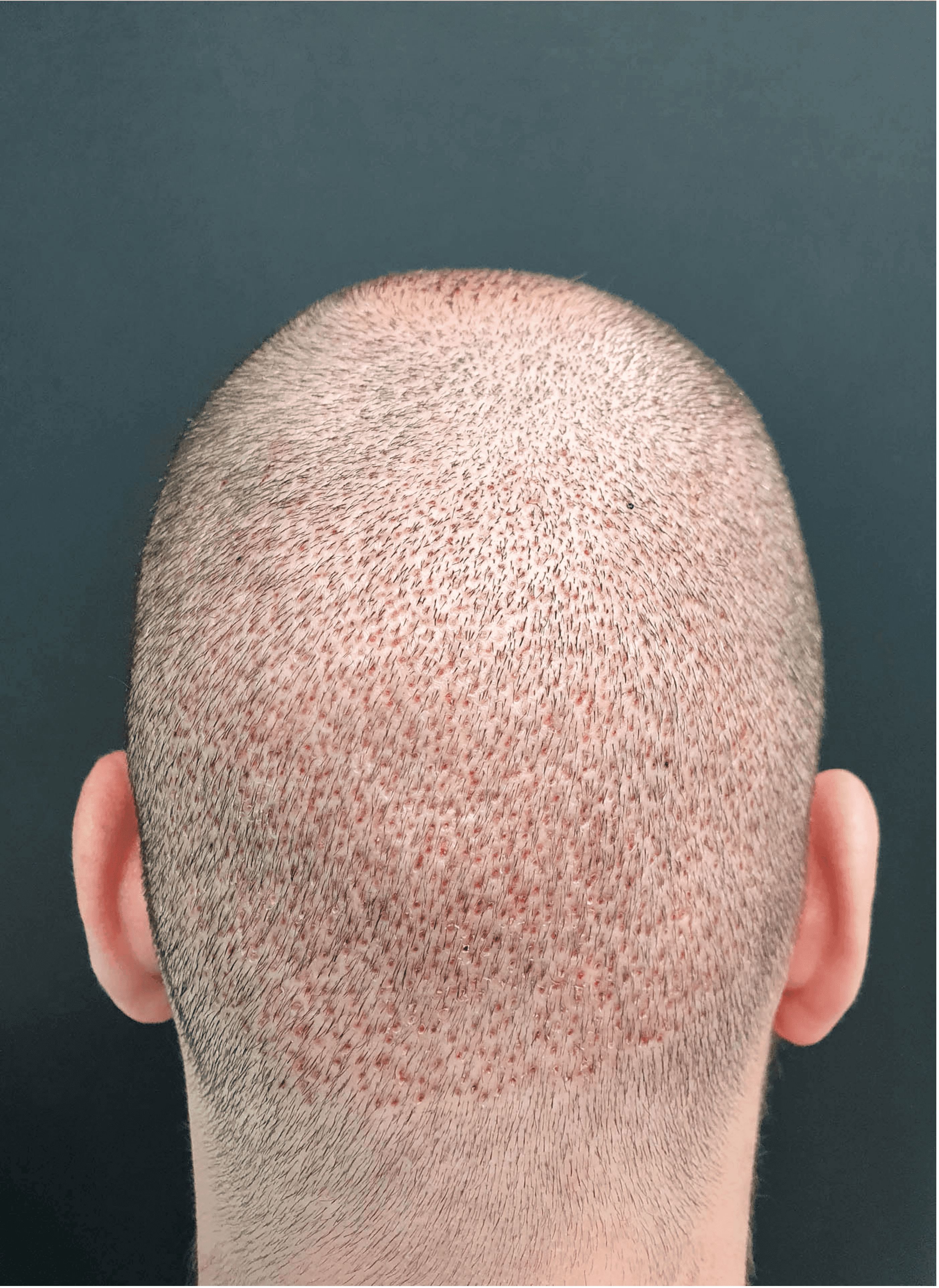
Photo 2. Donor area on the third day after the FUE hair transplant
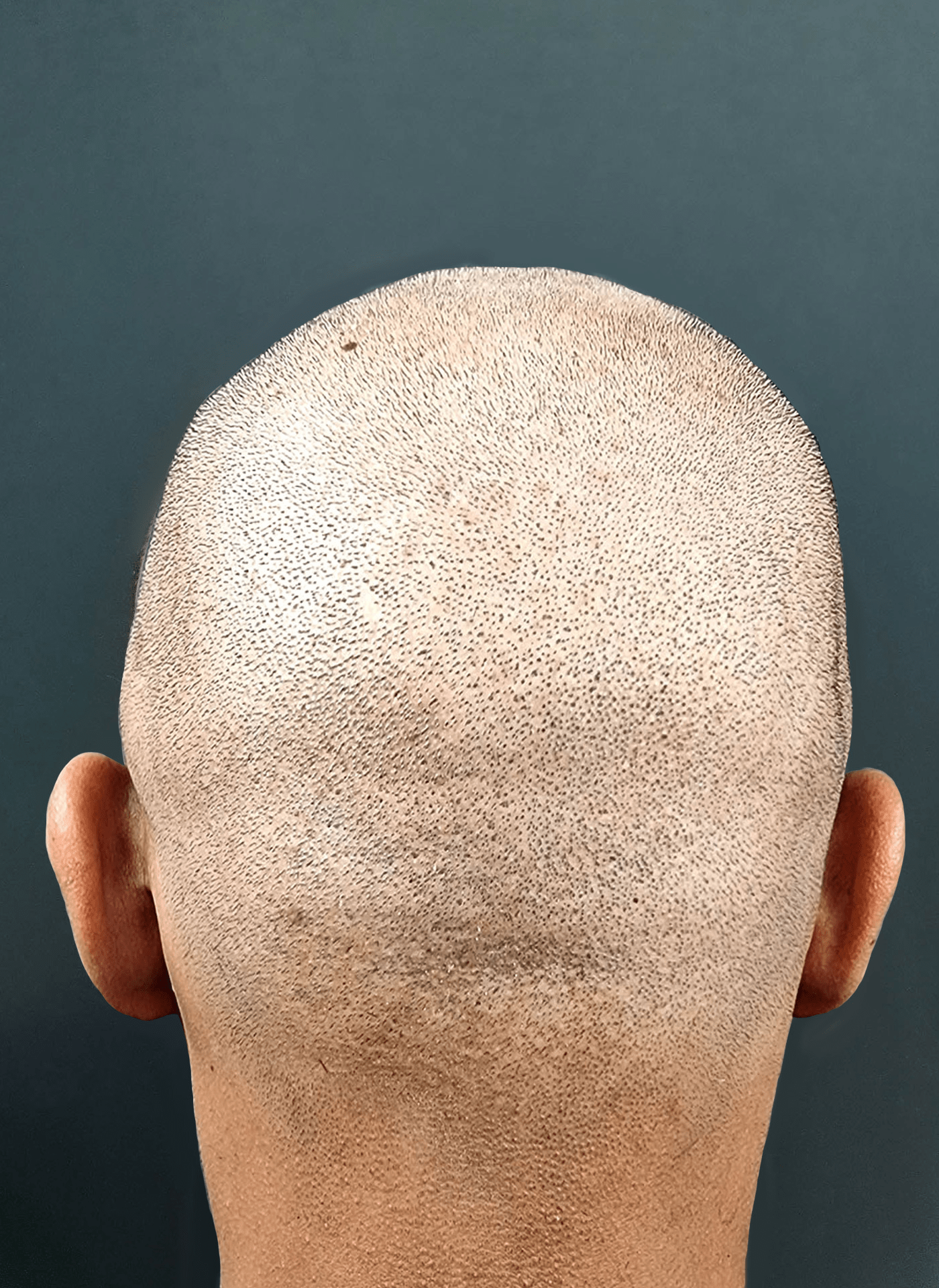

Photo 3. Donor area one year after the FUE hair transplant
FUE is considered to be the most modern hair transplantation technique, but in fact, it is far from that.
The FUE transplant era began with the famous publication by American hair transplant surgeons William Rassman and Robert Bernstein: "FUE Procedure - Minimally Invasive Surgery for Hair Transplantation" in the journal "Dermatologic Surgery" in 2002. After this article, the whole world started performing FUE transplant procedures. However, the first FUE procedures far predate Rassman and Bernstein. Dr. Shoji Okuda and Dr. Hajime Tamura used exactly the same technique during World War II. But unfortunately, their invaluable experience was lost because of the war. In the 50s of the XX century the American dermatologist Norman Orentreich “rediscovered” hair transplant surgery. He didn’t know anything about experience and researches of the Japanese doctors. Dr. Orentreich started to conduct hair transplant procedures by using 4 mm punches. Consequently, after transplanting 4 mm diameter grafts such hair plugs started to grow very unnaturally with “Toothbrush” and “Doll Head” effects (see photo 4). At the end of the 20th century Dr. Ray Woods began using small punches (up to 1 mm in diameter) for FUE transplant, but did not present or publish his work. Thus, Rassman and Bernstein are considered to be the pioneers of the FUE transplant method (see photos 5 and 6).
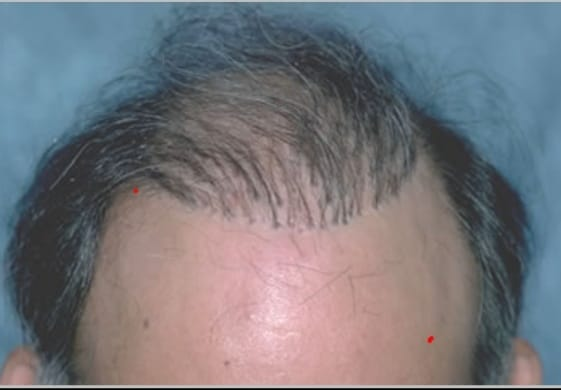
Photo 4. Hair plugs

Photo 5. A debate between William Rassman and Akaki Tsilosani at the experts round table at the ISHRS Meeting in Kuala Lumpur, 2014.

Photo 6. Robert Bernstein and Akaki Tsilosani at the ISHRS Meeting in Montreal, 2008.
FUE transplant is by far the most common and popular method of hair transplantation due to its obvious advantages.
Let’s make a comparison - FUE vs FUT:
1. With the FUE transplant technique, there are no incisions or stitches in the donor area and therefore no linear scar remains. This allows the patient to wear a very short haircut if desired.
2. FUE transplant is much less invasive than FUT, thus the postoperative period is more comfortable for the patients and as mentioned before FUE recovery timeline is shorter.
3. With FUE transplant follicular units can be harvested not just from the back of the head, but also from other parts of the body (chest, beard, groin, legs, etc.). This becomes extremely valuable when there is a poor donor supply on the back of the head.
4. During the patient’s first hair transplant procedure, the FUE transplant technique allows the surgeon to selectively extract grafts with more hair (follicles) to achieve a better result (Picture 7).
Photo 7. 7-Hair FUE graft harvested with the punch designed by Dr. Tsilosani
However, the FUE transplant technique also has many disadvantages:
1.Despite the lack of a linear scar on the back of the head, we cannot call FUE a completely “scarless” technique. After the FUE procedure, dot-like micro scars remain in the places where grafts were harvested. Since hair won’t grow in these micro scars, the hair density on the back of the head naturally decreases, and with large-scale hair transplants (harvesting 5000 grafts and more), depletion of the donor area or scarring may occur (see photos 8 and 9).
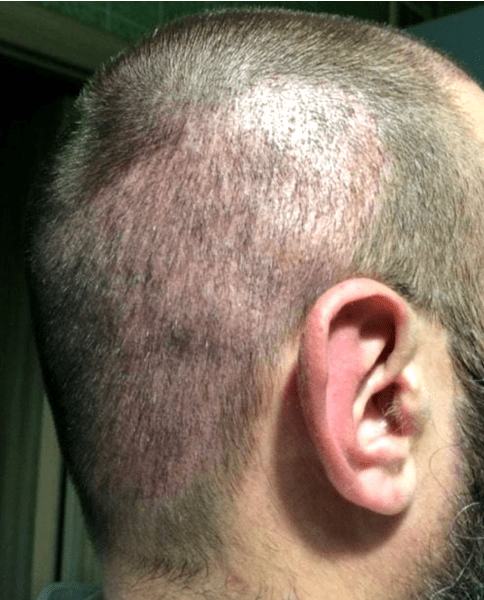
Photo 8. Depletion of donor area after aggressive harvesting of 5000 grafts by the FUE transplant method in one of the Turkish clinics
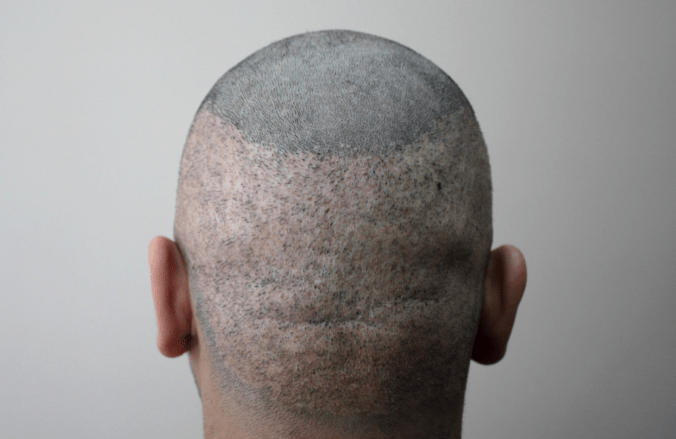

Photo 9. Complete scarring of the donor area after poor-quality harvesting of 9000 grafts by the FUE transplant method in one of the Turkish clinics
2.Due to the intrinsic nature of FUE transplantation, even the most experienced surgeons using the most modern equipment (punches and machines) will have a higher follicular transection (cutting, damage) rate than during the FUT hair transplant procedure (See photos 10 and 11).